
Navigating the intricate world of taxation can often feel like traversing a maze, with each state boasting its own set of rules and regulations. Among these, Hawaii stands out with its unique General Excise (GE) tax system. While most states rely on traditional sales taxes collected directly from consumers at the point of sale, Hawaii takes a different approach by imposing a tax on the gross income of businesses operating within its borders.
The General Excise Tax (GET), often referred to simply as GE tax, is a cornerstone of Hawaii’s revenue system. However, its complexity and broad reach have earned it a reputation for being one of the most perplexing tax systems in the United States. Both residents and businesses frequently find themselves grappling with its intricacies, often leading to confusion and frustration.
In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to demystify the nuances of GE sales tax in Hawaii. By shedding light on its intricacies, implications, and practical applications for businesses and consumers alike, we aim to provide clarity and understanding in a landscape often shrouded in uncertainty.
At its core, GE tax represents a departure from the conventional model of taxation seen in many other states. Instead of focusing solely on the final sale of goods and services to consumers, Hawaii’s tax system casts a much wider net, encompassing a broad spectrum of business activities. From wholesale transactions to service provision and even certain business inputs, GE tax applies across a diverse range of economic endeavors, making it a pervasive presence in the state’s commercial landscape.
Understanding the nuances of GE tax rates is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate Hawaii’s tax environment effectively. While the standard rate stands at 4%, variations exist depending on the nature of the transaction. For instance, wholesale transactions are subject to a lower rate of 0.5%, while certain activities, such as insurance commissions, may incur a higher rate of 0.15%. Moreover, exemptions exist for specific transactions, such as the sale of prescription drugs and certain food items, further complicating the tax landscape.
For businesses operating in Hawaii, compliance with GE tax regulations is not merely a matter of preference but a legal imperative. Failure to adhere to the intricate requirements set forth by the state can result in severe penalties and fines, underscoring the importance of meticulous record-keeping and accurate reporting. From tracking income and expenses to calculating and remitting the appropriate amount of GE tax, businesses must navigate a complex web of obligations to remain on the right side of the law.
Yet, the impact of GE tax extends beyond the realm of business, exerting a tangible influence on consumers’ everyday lives. While businesses shoulder the burden of paying GE tax, they often pass on a portion of this cost to consumers through higher prices. Consequently, the effective tax rate paid by consumers may surpass the nominal rate imposed on businesses, contributing to the overall cost of living in Hawaii.
As Hawaii grapples with economic and fiscal challenges, calls for reforming and modernizing the GE tax system have grown louder. Proponents advocate for changes aimed at enhancing fairness, efficiency, and transparency within the tax framework. By staying informed and engaged in discussions surrounding tax policy, businesses, policymakers, and individuals can collectively shape the future of Hawaii’s tax landscape.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of GE sales tax in Hawaii, exploring its implications for businesses and consumers alike. From exemptions and deductions to compliance challenges and potential alternatives, we will navigate the complexities of Hawaii’s tax system, empowering readers to navigate this often-daunting terrain with confidence and clarity.

Understanding General Excise Tax (GET):
Firstly, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concept of General Excise Tax (GET) in Hawaii. Unlike traditional sales taxes found in most states, which are imposed on consumers at the point of sale, GET is a tax on the gross income of businesses operating in Hawaii. This means that businesses are responsible for paying the tax, although they may pass on some or all of the burden to consumers through higher prices.
The Unique Structure of GE Tax:
One of the distinctive features of GE tax is its broad reach. Unlike traditional sales taxes, which typically apply to the final sale of goods and services to consumers, GE tax applies to a wide range of business activities, including wholesale transactions, services, and even certain business inputs. This broad base allows the state to generate significant revenue while keeping individual tax rates relatively low.
GE Tax Rates:
As of 2024, the standard GE tax rate in Hawaii is 4%. However, it’s essential to note that different activities may be subject to different tax rates. For example, wholesale transactions are taxed at a lower rate of 0.5%, while certain activities, such as insurance commissions, are taxed at a higher rate of 0.15%. Additionally, some transactions may be exempt from GE tax altogether, such as sales of prescription drugs and certain food items.
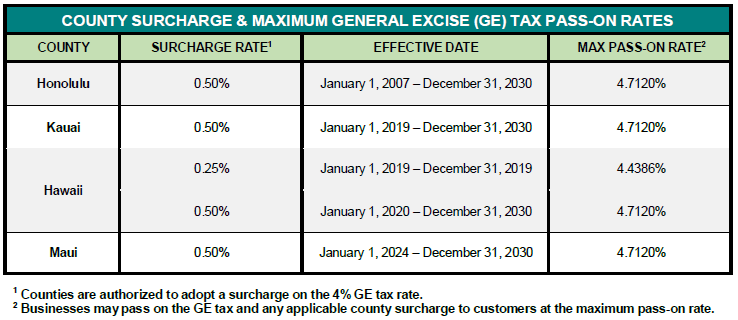
Practical Implications for Businesses:
For businesses operating in Hawaii, understanding and complying with GE tax regulations is crucial. Failure to do so can result in hefty penalties and fines. Therefore, businesses must keep detailed records of their income and expenses, including any GE tax collected or paid. Additionally, businesses must ensure that they accurately calculate and remit the appropriate amount of GE tax to the state on a regular basis.
Impact on Consumers:
While businesses are responsible for paying GE tax, the burden often falls on consumers in the form of higher prices. Since businesses may pass on some or all of the cost of GE tax to consumers, the effective tax rate paid by consumers may be higher than the nominal rate imposed on businesses. This can have a significant impact on the cost of living in Hawaii, particularly for low-income individuals and families.
Navigating Exemptions and Deductions:
Like any tax system, GE tax in Hawaii offers certain exemptions and deductions that businesses can take advantage of to reduce their tax liability. For example, certain types of income, such as dividends and interest, may be exempt from GE tax altogether. Additionally, businesses may be able to deduct certain expenses, such as the cost of goods sold, from their gross income before calculating their tax liability.
Compliance Challenges:
Complying with GE tax regulations can be challenging for businesses, especially smaller enterprises with limited resources. The complexity of the tax code, coupled with the administrative burden of record-keeping and reporting, can make it difficult for businesses to ensure full compliance with the law. As a result, some businesses may inadvertently underreport their income or overstate their deductions, leading to potential audit issues and legal consequences.
Recent Developments and Reforms:
In recent years, there have been calls for reforming Hawaii’s GE tax system to make it more equitable and efficient. Some advocates have proposed lowering the overall tax rate while broadening the base to include more economic activities. Others have called for simplifying the tax code and reducing administrative burdens on businesses. While there have been some minor changes to the GE tax system in recent years, significant reforms have yet to materialize.
The Economic Impact of GE Tax:
GE tax plays a crucial role in Hawaii’s economy, generating significant revenue for the state government. This revenue helps fund essential services and infrastructure projects, such as education, healthcare, and transportation. However, critics argue that GE tax may also have negative economic consequences, such as discouraging investment and entrepreneurship. Additionally, the regressive nature of GE tax means that low-income individuals and families may bear a disproportionate burden compared to wealthier individuals and corporations.
Navigating GE Tax as a Small Business Owner:
For small business owners in Hawaii, understanding and managing GE tax obligations is essential for long-term success. While the complexity of the tax code may seem daunting, there are resources available to help businesses navigate the process. For example, the Hawaii Department of Taxation provides guidance and assistance to businesses on compliance issues related to GE tax. Additionally, hiring a qualified tax professional can help ensure that businesses accurately report their income and expenses and minimize their tax liability.
Potential Alternatives to GE Tax:
Given the challenges associated with GE tax, some policymakers and economists have proposed alternative approaches to taxation in Hawaii. For example, some have suggested replacing GE tax with a more traditional sales tax that is levied directly on consumers at the point of sale. Others have proposed implementing a progressive income tax system that would tax individuals and corporations based on their ability to pay. While these alternatives have their own advantages and disadvantages, they highlight the need for continued debate and discussion on tax policy in Hawaii.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, navigating the General Excise (GE) sales tax system in Hawaii requires a deep understanding of its complexities and implications for both businesses and consumers. The broad reach and unique structure of GE tax present challenges that necessitate careful compliance and strategic planning. Businesses must diligently track their income and expenses, ensuring accurate reporting and remittance of GE tax to avoid penalties and fines. Similarly, consumers should be mindful of how GE tax can affect prices and the overall cost of living in Hawaii, as it indirectly impacts their wallets.
As Hawaii grapples with ongoing economic and fiscal challenges, the need for reform and modernization of the GE tax system becomes increasingly apparent. Addressing the shortcomings of the current system and exploring alternatives could lead to a fairer and more sustainable tax framework that supports economic growth and prosperity for all residents.
It is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals to stay informed and engaged in discussions surrounding tax policy in Hawaii. By advocating for reforms and collaborating on solutions, we can work towards creating a tax system that fosters fairness, transparency, and economic opportunity.
For businesses seeking expert guidance and assistance in managing their financial obligations, including navigating GE tax compliance, Amazing Financial Solutions offers comprehensive support and tailored solutions. Visit Amazing Financial Solutions to learn more about how their expertise can help your business thrive in Hawaii’s dynamic economic landscape. Let’s work together to build a brighter financial future for Hawaii’s businesses and communities.
